The job of a purchaser: These tasks await you
In conjunction with digitization, procurement has seen substantial changes. In its modern form, it is a fundamental factor for a company's success. This can be attributed to the technical development, that allows for new, often strategic assignments. Hence, the job profile and the requirements buyers have to meet have changed immensely.
While a few years ago, they were frequently just using manually administrated order sheets or Excel tables, buyers now have mostly digital tools at their disposal. Thanks to these tools, purchasing can assume a heftier role earlier and become more visible within the enterprise.
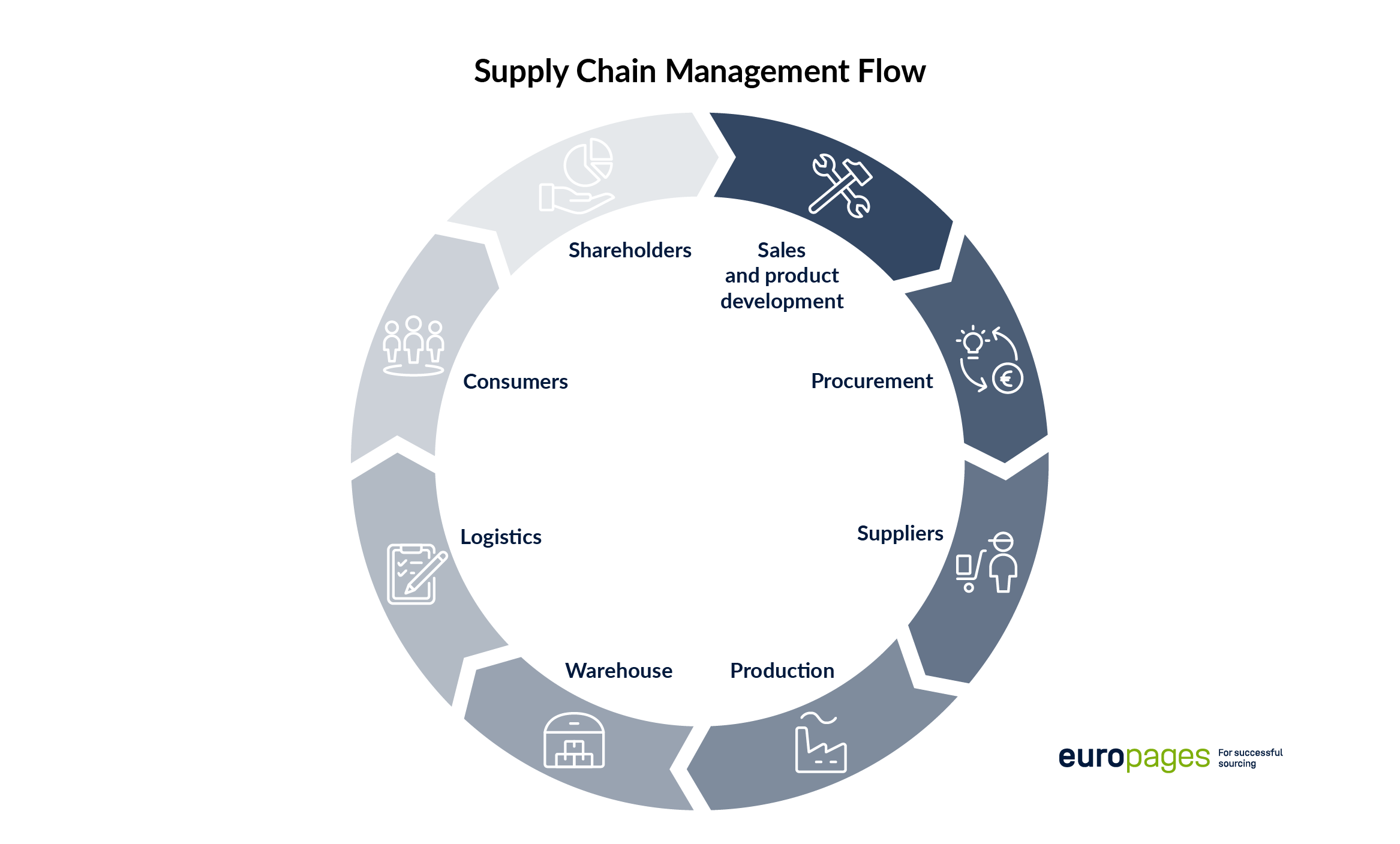
Nowadays, procurement views itself as a strategic interface in the supply chain. This means that it does not only handle internal and external needs, but also increasingly assumes the role of a central data supplier for the entire company. Hence, the profession now requires the following of buyers:
- They constantly scan the procurement market and are informed of the developments and prices, margins of suppliers and manufacturers, in-house needs and production processes.
- From the overview, they anticipate future scenarios to detect changing conditions early on and to be able to respond to them. The focus is always on the best price-performance ratio.
- They therefore collect, organise and analyse relevant data for more than their own department. Buyers prepare information also for strategic purposes on behalf of the executive management, sales, production, development and logistics. The buyer assumes the position of a consultant.
- Buyers view themselves as the interface to all stakeholders within the supply chain and they constantly monitor their reliability. If they establish any problems, they need to be able to act to remedy these as quickly as possible. If any suppliers become unavailable, their job is to quickly find substitutes.
- They are always up to date on the status of the warehouse, production and also ensure timely replenishments at the best possible terms.
- They handle returns and complaints, and therefore also play a key role in customer satisfaction.
- Whenever it makes sense, the introduce automated processes that give them more leeway for strategic tasks.
- They control all relevant processes and measures, generate related data, check the data and initiate optimizations based on analysis.
- They handle all of that and more using digital tools that are often synched with interfaces to other programs. For instance, the simultaneous exchange of data and other information with both, internal and external stakeholders can be processed through multiple channels.
The listed tasks impose different requirements on buyers. They don't just need specialist knowledge, but also good personal and social skills. More details below.
Present your company on our platform!
The advantages:
- International audience and visibility
- Set-up in 5 minutes
- Numerous options and services through individual content
Mandatory competencies in procurement: The hard skills
The fundamental tools in purchasing: substantial expertise on multiple levels. The key hard skills perferably include:
- A degree in IT or business
- Confidence using IT and PPS systems (e.g. ERP systems).
- Industry knowledge
- Expertise in procurement, product group, logistics and supplier management and related processes
- Qualified knowledge in trade, services and manufacturing technology
- Business-fluent foreign language skills
- Expertise in disciplines such as market research and statistics, product and project management, organization and controlling
Useful soft skills for purchasers
Besides the abovementioned expertise, the requirements buyers must meet also include added individual strengths that arise from the character and personality of an individual. These ideally include:
- Team player
- Communications and negotiation skills
- Compelling attitude
- Flexibility
- Ability to handle stress
- Empathy
- Ability to accept and give criticism
- Self-driven attitude
- Methodical competencies (e.g. in risk management, interface management, supplier relations management, strategic development, analysis


